Extrusion Bioprinting
3D extrusion bioprinting is an additive manufacturing technology where biomaterials, terms bioinks, are deposited in a three dimensional space in a layer-by-layer fashion. 3D extrusion bioprinters are as low cost, desktop models and more advanced industrial models. At TEB we work towards hardware improvements to improve accuracy and reliability of the print, but our main focus is on the development of novel bioprinting materials including microgel based and nanocomposite inks. Our laboratory is investigating new ways and materials to employ 3D bioprinting as a technology for tissue engineering.
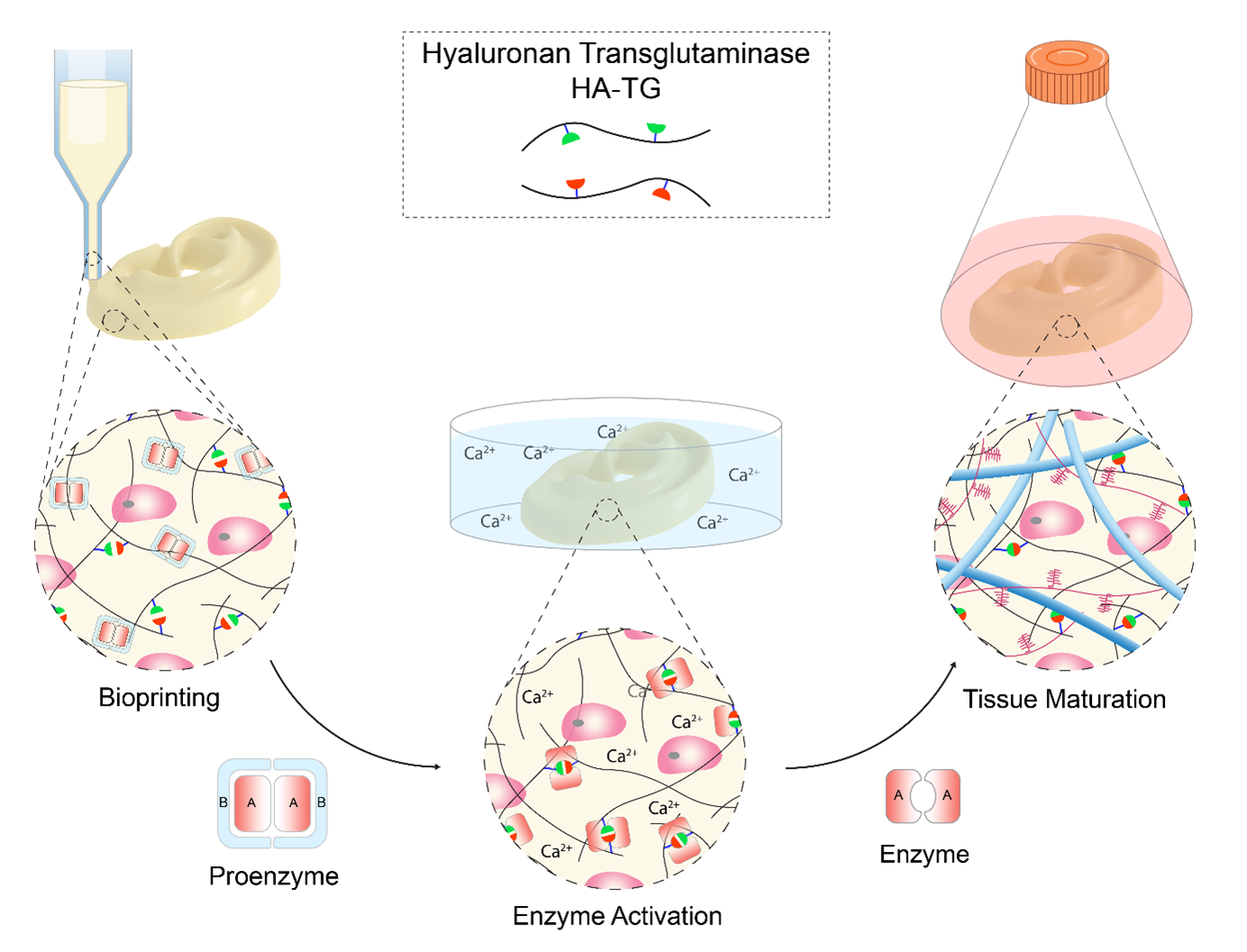
Enzymatically crosslinkable bioinks offer a fully biocompatible polymerization mechanism by recapitulating the body's own wound healing response. Enzymatic crosslinking further allows the incorporation of natural features such as signaling molecules and the creation of modular architectures of different hydrogel systems. Ultimately we aim to engineer tissue which can recapitulate natural tissue in its function.
Publications:
- Bioprinting of Cartilaginous Auricular Constructs Utilizing an Enzymatically Crosslinkable Bioink, P Fisch, N Broguiere, S Finkielsztein, T Linder, M Zenobi‐Wong, Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, external page https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202008261
Contact
Gewebetechnol. und Biofabrikation
Otto-Stern-Weg 7
8093
Zürich
Switzerland
Contact
No database information available